
题目描述
在一个 n x n 的整数矩阵 grid 中,每一个方格的值 grid[i][j] 表示位置 (i, j) 的平台高度。
当开始下雨时,在时间为 t 时,水池中的水位为 t 。你可以从一个平台游向四周相邻的任意一个平台,但是前提是此时水位必须同时淹没这两个平台。假定你可以瞬间移动无限距离,也就是默认在方格内部游动是不耗时的。当然,在你游泳的时候你必须待在坐标方格里面。
你从坐标方格的左上平台 (0,0) 出发。返回 你到达坐标方格的右下平台 (n-1, n-1) 所需的最少时间 。
示例 1:
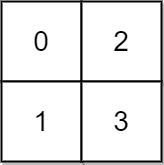
输入: grid = [[0,2],[1,3]]
输出: 3
解释:
时间为0时,你位于坐标方格的位置为 (0, 0)。
此时你不能游向任意方向,因为四个相邻方向平台的高度都大于当前时间为 0 时的水位。
等时间到达 3 时,你才可以游向平台 (1, 1). 因为此时的水位是 3,坐标方格中的平台没有比水位 3 更高的,所以你可以游向坐标方格中的任意位置
示例 2:
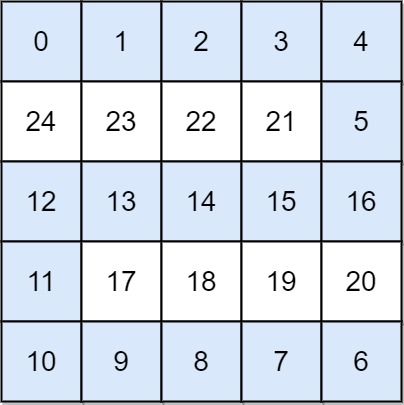
输入: grid = [[0,1,2,3,4],[24,23,22,21,5],[12,13,14,15,16],[11,17,18,19,20],[10,9,8,7,6]]
输出: 16
解释: 最终的路线用加粗进行了标记。
我们必须等到时间为 16,此时才能保证平台 (0, 0) 和 (4, 4) 是连通的
提示:
n == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= n <= 500 <= grid[i][j] < n2grid[i][j] 中每个值 均无重复
解法
方法一:并查集
我们可以将每个位置 \((i, j)\) 映射为一个编号 \(id = i \times n + j\),并使用并查集维护连通分量。
我们首先用一个一维数组 \(hi\) 记录每个高度对应的位置编号,即 \(hi[h]\) 表示高度为 \(h\) 的位置编号。
然后我们从高度 \(0\) 开始遍历到高度 \(n^2 - 1\),对于每个高度 \(t\),我们将位置 \(hi[t]\) 与其四个相邻且高度不超过 \(t\) 的位置进行合并。如果合并后,位置 \(0\) 和位置 \(n^2 - 1\) 连通了,那么我们就找到了最小的时间 \(t\),返回 \(t\) 即可。
时间复杂度 \(O(n^2 \times \log n)\),空间复杂度 \(O(n^2)\)。其中 \(n\) 是矩阵的边长。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24 | class Solution:
def swimInWater(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
def find(x: int) -> int:
if p[x] != x:
p[x] = find(p[x])
return p[x]
n = len(grid)
m = n * n
p = list(range(m))
hi = [0] * m
for i, row in enumerate(grid):
for j, h in enumerate(row):
hi[h] = i * n + j
dirs = (-1, 0, 1, 0, -1)
for t in range(m):
x, y = divmod(hi[t], n)
for dx, dy in pairwise(dirs):
nx, ny = x + dx, y + dy
if 0 <= nx < n and 0 <= ny < n and grid[nx][ny] <= t:
p[find(x * n + y)] = find(nx * n + ny)
if find(0) == find(m - 1):
return t
return 0
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41 | class Solution {
public int swimInWater(int[][] grid) {
int n = grid.length;
int m = n * n;
int[] p = new int[m];
Arrays.setAll(p, i -> i);
IntUnaryOperator find = new IntUnaryOperator() {
@Override
public int applyAsInt(int x) {
if (p[x] != x) p[x] = applyAsInt(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
};
int[] hi = new int[m];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
hi[grid[i][j]] = i * n + j;
}
}
int[] dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
for (int t = 0; t < m; t++) {
int id = hi[t];
int x = id / n, y = id % n;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int nx = x + dirs[k], ny = y + dirs[k + 1];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < n && ny >= 0 && ny < n && grid[nx][ny] <= t) {
int a = find.applyAsInt(x * n + y);
int b = find.applyAsInt(nx * n + ny);
p[a] = b;
}
}
if (find.applyAsInt(0) == find.applyAsInt(m - 1)) {
return t;
}
}
return 0;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42 | class Solution {
public:
int swimInWater(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int n = grid.size();
int m = n * n;
vector<int> p(m);
iota(p.begin(), p.end(), 0);
auto find = [&](this auto&& find, int x) -> int {
if (p[x] != x) {
p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
return p[x];
};
vector<int> hi(m);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
hi[grid[i][j]] = i * n + j;
}
}
array<int, 5> dirs{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
for (int t = 0; t < m; ++t) {
int id = hi[t];
int x = id / n, y = id % n;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int nx = x + dirs[k], ny = y + dirs[k + 1];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < n && ny >= 0 && ny < n && grid[nx][ny] <= t) {
int a = find(x * n + y);
int b = find(nx * n + ny);
p[a] = b;
}
}
if (find(0) == find(m - 1)) {
return t;
}
}
return 0;
}
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38 | func swimInWater(grid [][]int) int {
n := len(grid)
m := n * n
p := make([]int, m)
for i := range p {
p[i] = i
}
var find func(int) int
find = func(x int) int {
if p[x] != x {
p[x] = find(p[x])
}
return p[x]
}
hi := make([]int, m)
for i := range grid {
for j, h := range grid[i] {
hi[h] = i*n + j
}
}
dirs := []int{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}
for t := 0; t < m; t++ {
id := hi[t]
x, y := id/n, id%n
for k := 0; k < 4; k++ {
nx, ny := x+dirs[k], y+dirs[k+1]
if nx >= 0 && nx < n && ny >= 0 && ny < n && grid[nx][ny] <= t {
a := find(x*n + y)
b := find(nx*n + ny)
p[a] = b
}
}
if find(0) == find(m-1) {
return t
}
}
return 0
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34 | function swimInWater(grid: number[][]): number {
const n = grid.length;
const m = n * n;
const p = Array.from({ length: m }, (_, i) => i);
const hi = new Array<number>(m);
const find = (x: number): number => (p[x] === x ? x : (p[x] = find(p[x])));
for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
hi[grid[i][j]] = i * n + j;
}
}
const dirs = [-1, 0, 1, 0, -1];
for (let t = 0; t < m; ++t) {
const id = hi[t];
const x = Math.floor(id / n);
const y = id % n;
for (let k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
const nx = x + dirs[k];
const ny = y + dirs[k + 1];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < n && ny >= 0 && ny < n && grid[nx][ny] <= t) {
p[find(x * n + y)] = find(nx * n + ny);
}
}
if (find(0) === find(m - 1)) {
return t;
}
}
return 0;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49 | impl Solution {
pub fn swim_in_water(grid: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
let n = grid.len();
let m = n * n;
let mut p: Vec<usize> = (0..m).collect();
let mut hi = vec![0usize; m];
for i in 0..n {
for j in 0..n {
hi[grid[i][j] as usize] = i * n + j;
}
}
fn find(x: usize, p: &mut Vec<usize>) -> usize {
if p[x] != x {
p[x] = find(p[x], p);
}
p[x]
}
let dirs = [-1isize, 0, 1, 0, -1];
for t in 0..m {
let id = hi[t];
let x = id / n;
let y = id % n;
for k in 0..4 {
let nx = x as isize + dirs[k];
let ny = y as isize + dirs[k + 1];
if nx >= 0 && nx < n as isize && ny >= 0 && ny < n as isize {
let nx = nx as usize;
let ny = ny as usize;
if grid[nx][ny] as usize <= t {
let a = find(x * n + y, &mut p);
let b = find(nx * n + ny, &mut p);
p[a] = b;
}
}
}
if find(0, &mut p) == find(m - 1, &mut p) {
return t as i32;
}
}
0
}
}
|


