排序 数学 数组 矩阵
题目描述 给你一个 m x n 的二进制网格 grid ,其中 1 表示某个朋友的家所处的位置。返回 最小的 总行走距离 。
总行走距离 是朋友们家到碰头地点的距离之和。
我们将使用 曼哈顿距离 来计算,其中 distance(p1, p2) = |p2.x - p1.x| + |p2.y - p1.y| 。
示例 1:
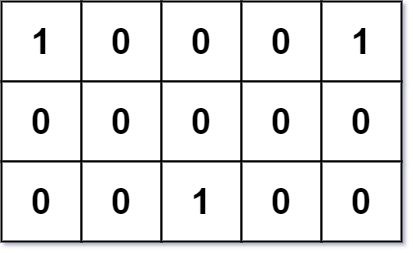
输入: grid = [[1,0,0,0,1],[0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,1,0,0]]
输出: 6
解释: 给定的三个人分别住在(0,0),(0,4) 和 (2,2):
(0,2) 是一个最佳的碰面点,其总行走距离为 2 + 2 + 2 = 6,最小,因此返回 6。 示例 2:
输入: grid = [[1,1]]
输出: 1
提示:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 200grid[i][j] == 0 or 1.grid 中 至少 有两个朋友 解法 方法一:排序 + 中位数 对于每一行,我们可以将所有的 \(1\) 的下标排序,然后取中位数 \(i\) 作为碰头地点的横坐标。
对于每一列,我们可以将所有的 \(1\) 的下标排序,然后取中位数 \(i\) 作为碰头地点的纵坐标。
最后,我们计算所有 \(1\) 到碰头地点 \((i, j)\) 的曼哈顿距离之和即可。
时间复杂度 \(O(m\times n\times \log(m\times n))\) 。最多有 \(m\times n\) 个 \(1\) ,排序的时间复杂度为 \(\log(m\times n)\) 。
相似题目:
Python3 Java C++ Go Rust
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15 class Solution :
def minTotalDistance ( self , grid : List [ List [ int ]]) -> int :
def f ( arr , x ):
return sum ( abs ( v - x ) for v in arr )
rows , cols = [], []
for i , row in enumerate ( grid ):
for j , v in enumerate ( row ):
if v :
rows . append ( i )
cols . append ( j )
cols . sort ()
i = rows [ len ( rows ) >> 1 ]
j = cols [ len ( cols ) >> 1 ]
return f ( rows , i ) + f ( cols , j )
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27 class Solution {
public int minTotalDistance ( int [][] grid ) {
int m = grid . length , n = grid [ 0 ] . length ;
List < Integer > rows = new ArrayList <> ();
List < Integer > cols = new ArrayList <> ();
for ( int i = 0 ; i < m ; ++ i ) {
for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; ++ j ) {
if ( grid [ i ][ j ] == 1 ) {
rows . add ( i );
cols . add ( j );
}
}
}
Collections . sort ( cols );
int i = rows . get ( rows . size () >> 1 );
int j = cols . get ( cols . size () >> 1 );
return f ( rows , i ) + f ( cols , j );
}
private int f ( List < Integer > arr , int x ) {
int s = 0 ;
for ( int v : arr ) {
s += Math . abs ( v - x );
}
return s ;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27 class Solution {
public :
int minTotalDistance ( vector < vector < int >>& grid ) {
int m = grid . size (), n = grid [ 0 ]. size ();
vector < int > rows ;
vector < int > cols ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < m ; ++ i ) {
for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; ++ j ) {
if ( grid [ i ][ j ]) {
rows . emplace_back ( i );
cols . emplace_back ( j );
}
}
}
sort ( cols . begin (), cols . end ());
int i = rows [ rows . size () / 2 ];
int j = cols [ cols . size () / 2 ];
auto f = []( vector < int >& arr , int x ) {
int s = 0 ;
for ( int v : arr ) {
s += abs ( v - x );
}
return s ;
};
return f ( rows , i ) + f ( cols , j );
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29 func minTotalDistance ( grid [][] int ) int {
rows , cols := [] int {}, [] int {}
for i , row := range grid {
for j , v := range row {
if v == 1 {
rows = append ( rows , i )
cols = append ( cols , j )
}
}
}
sort . Ints ( cols )
i := rows [ len ( rows ) >> 1 ]
j := cols [ len ( cols ) >> 1 ]
f := func ( arr [] int , x int ) int {
s := 0
for _ , v := range arr {
s += abs ( v - x )
}
return s
}
return f ( rows , i ) + f ( cols , j )
}
func abs ( x int ) int {
if x < 0 {
return - x
}
return x
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37 impl Solution {
#[allow(dead_code)]
pub fn min_total_distance ( grid : Vec < Vec < i32 >> ) -> i32 {
let n = grid . len ();
let m = grid [ 0 ]. len ();
let mut row_vec = Vec :: new ();
let mut col_vec = Vec :: new ();
// Initialize the two vector
for i in 0 .. n {
for j in 0 .. m {
if grid [ i ][ j ] == 1 {
row_vec . push ( i as i32 );
col_vec . push ( j as i32 );
}
}
}
// Since the row vector is originally sorted, we only need to sort the col vector here
col_vec . sort ();
Self :: compute_manhattan_dis ( & row_vec , row_vec [ row_vec . len () / 2 ])
+ Self :: compute_manhattan_dis ( & col_vec , col_vec [ col_vec . len () / 2 ])
}
#[allow(dead_code)]
fn compute_manhattan_dis ( v : & Vec < i32 > , e : i32 ) -> i32 {
let mut ret = 0 ;
for num in v {
ret += ( num - e ). abs ();
}
ret
}
}