二叉树 哈希表 树 深度优先搜索
题目描述 给定一棵二叉树的根节点 root 和 TreeNode 类对象的数组(列表) nodes,返回 nodes 中所有节点的最近公共祖先(LCA)。数组(列表)中所有节点都存在于该二叉树中,且二叉树中所有节点的值都是互不相同的。
我们扩展二叉树的最近公共祖先节点在维基百科上的定义 :“对于任意合理的 i 值, n 个节点 p1 、 p2 、...、 pn 在二叉树 T 中的最近公共祖先节点是后代 中包含所有节点 pi 的最深节点(我们允许一个节点是其自身的后代)”。一个节点 x 的后代节点是节点 x 到某一叶节点间的路径中的节点 y。
示例 1:
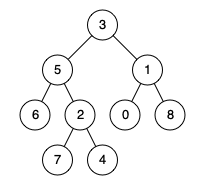
输入: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], nodes = [4,7]
输出: 2
解释: 节点 4 和 7 的最近公共祖先是 2。
示例 2:
输入: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], nodes = [1]
输出: 1
解释: 单个节点的最近公共祖先是该节点本身。
示例 3:
输入: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], nodes = [7,6,2,4]
输出: 5
解释: 节点 7、6、2 和 4 的最近公共祖先节点是 5。
示例 4:
输入: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], nodes = [0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]
输出: 3
解释: 树中所有节点的最近公共祖先是根节点。
提示:
树中节点个数的范围是 [1, 104 ] 。 -109 <= Node.val <= 109 所有的 Node.val 都是互不相同 的。 所有的 nodes[i] 都存在于该树中。 所有的 nodes[i] 都是互不相同的。 解法 方法一:哈希表 + DFS 我们用一个哈希表 \(\textit{s}\) 记录数组 \(\textit{nodes}\) 中所有节点的值,然后使用深度优先搜索,当遍历到的节点为空或者节点的值在哈希表 \(\textit{s}\) 中时,返回当前节点。否则,递归遍历左右子树,如果左右子树的返回值都不为空,说明当前节点就是最近公共祖先,否则返回不为空的那个子树的返回值。
时间复杂度 \(O(n + m)\) ,空间复杂度 \(O(n + m)\) 。其中 \(n\) 和 \(m\) 分别是二叉树的节点数和数组 \(\textit{nodes}\) 的长度。
Python3 Java C++ JavaScript
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22 # Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution :
def lowestCommonAncestor (
self , root : 'TreeNode' , nodes : 'List[TreeNode]'
) -> 'TreeNode' :
def dfs ( root ):
if root is None or root . val in s :
return root
left , right = dfs ( root . left ), dfs ( root . right )
if left and right :
return root
return left or right
s = { node . val for node in nodes }
return dfs ( root )
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private Set < Integer > s = new HashSet <> ();
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor ( TreeNode root , TreeNode [] nodes ) {
for ( TreeNode node : nodes ) {
s . add ( node . val );
}
return dfs ( root );
}
private TreeNode dfs ( TreeNode root ) {
if ( root == null || s . contains ( root . val )) {
return root ;
}
TreeNode left = dfs ( root . left );
TreeNode right = dfs ( root . right );
if ( left == null ) {
return right ;
}
if ( right == null ) {
return left ;
}
return root ;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public :
TreeNode * lowestCommonAncestor ( TreeNode * root , vector < TreeNode *>& nodes ) {
unordered_set < int > s ;
for ( auto node : nodes ) {
s . insert ( node -> val );
}
auto dfs = [ & ]( this auto && dfs , TreeNode * root ) -> TreeNode * {
if ( ! root || s . contains ( root -> val )) {
return root ;
}
auto left = dfs ( root -> left );
auto right = dfs ( root -> right );
if ( ! left ) {
return right ;
}
if ( ! right ) {
return left ;
}
return root ;
};
return dfs ( root );
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {TreeNode[]} nodes
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var lowestCommonAncestor = function ( root , nodes ) {
const s = new Set ();
for ( const node of nodes ) {
s . add ( node . val );
}
function dfs ( root ) {
if ( ! root || s . has ( root . val )) {
return root ;
}
const [ left , right ] = [ dfs ( root . left ), dfs ( root . right )];
if ( left && right ) {
return root ;
}
return left || right ;
}
return dfs ( root );
};
GitHub