二叉树 树 深度优先搜索
题目描述 给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个整数 limit ,请你同时删除树中所有 不足节点 ,并返回最终二叉树的根节点。
假如通过节点 node 的每种可能的 “根-叶” 路径上值的总和全都小于给定的 limit,则该节点被称之为 不足节点 ,需要被删除。
叶子节点 ,就是没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
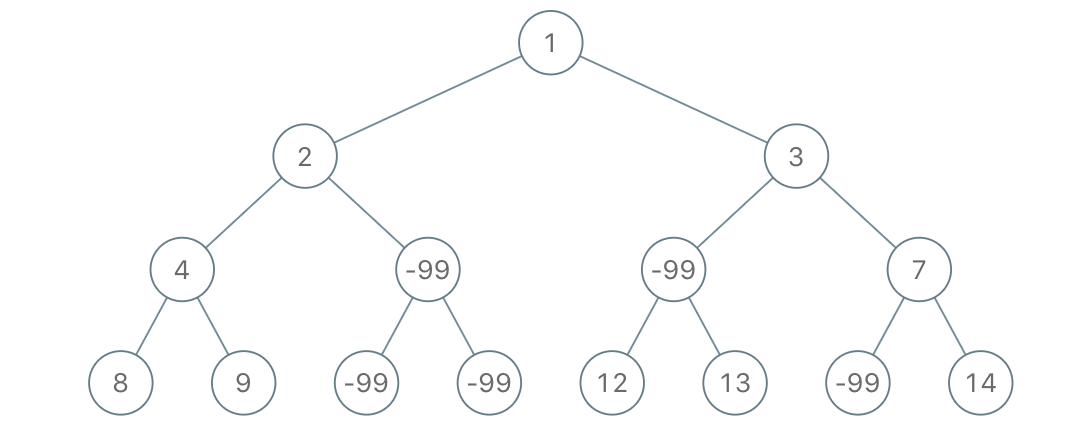
输入: root = [1,2,3,4,-99,-99,7,8,9,-99,-99,12,13,-99,14], limit = 1
输出: [1,2,3,4,null,null,7,8,9,null,14]
示例 2:
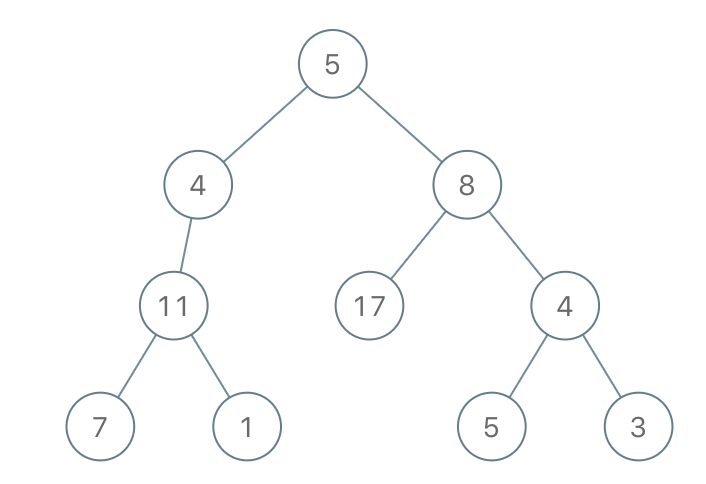
输入: root = [5,4,8,11,null,17,4,7,1,null,null,5,3], limit = 22
输出: [5,4,8,11,null,17,4,7,null,null,null,5]
示例 3:
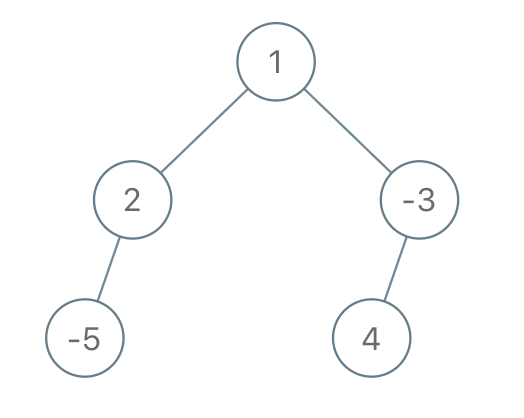
输入: root = [1,2,-3,-5,null,4,null], limit = -1
输出: [1,null,-3,4]
提示:
树中节点数目在范围 [1, 5000] 内 -105 <= Node.val <= 105 -109 <= limit <= 109
解法 方法一:递归 我们递归遍历整棵树,对于当前遍历到的节点 \(root\) :
如果 \(root\) 为空,那么返回空;否则,我们将 \(limit\) 减去当前节点的值,即 \(limit = limit - root.val\) ,然后继续执行下述步骤。
如果 \(root\) 为叶子节点(即 \(root\) 的左右子节点都为空),说明我们已经走完了一条从根节点到叶子节点的路径。如果此时 \(limit \gt 0\) ,说明该路径上所有节点的值的和小于 \(limit\) ,我们返回空节点,表示删除;否则,说明该路径上所有节点的值的和大于等于 \(limit\) ,我们返回 \(root\) 。
如果 \(root\) 不是叶子节点,那么我们递归调用函数 \(sufficientSubset\) ,对 \(root\) 的左右子节点分别进行处理,并将返回值分别赋值给 \(root\) 的左右子节点。
如果 \(root\) 的左右子节点在经过递归调用后变成了空节点,那么说明 \(root\) 的左右子树中所有从根节点到叶子节点的路径上所有节点的值的和都小于 \(limit\) ,因此我们返回空节点,表示删除 \(root\) ;否则,说明 \(root\) 的左右子树中存在从根节点到叶子节点上所有节点值的和大于等于 \(limit\) 的路径,因此我们返回 \(root\) 。
时间复杂度 \(O(n)\) ,空间复杂度 \(O(n)\) 。其中 \(n\) 是二叉树的节点个数。
Python3 Java C++ Go TypeScript JavaScript
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18 # Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution :
def sufficientSubset (
self , root : Optional [ TreeNode ], limit : int
) -> Optional [ TreeNode ]:
if root is None :
return None
limit -= root . val
if root . left is None and root . right is None :
return None if limit > 0 else root
root . left = self . sufficientSubset ( root . left , limit )
root . right = self . sufficientSubset ( root . right , limit )
return None if root . left is None and root . right is None else root
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode sufficientSubset ( TreeNode root , int limit ) {
if ( root == null ) {
return null ;
}
limit -= root . val ;
if ( root . left == null && root . right == null ) {
return limit > 0 ? null : root ;
}
root . left = sufficientSubset ( root . left , limit );
root . right = sufficientSubset ( root . right , limit );
return root . left == null && root . right == null ? null : root ;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public :
TreeNode * sufficientSubset ( TreeNode * root , int limit ) {
if ( ! root ) {
return nullptr ;
}
limit -= root -> val ;
if ( ! root -> left && ! root -> right ) {
return limit > 0 ? nullptr : root ;
}
root -> left = sufficientSubset ( root -> left , limit );
root -> right = sufficientSubset ( root -> right , limit );
return ! root -> left && ! root -> right ? nullptr : root ;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func sufficientSubset ( root * TreeNode , limit int ) * TreeNode {
if root == nil {
return nil
}
limit -= root . Val
if root . Left == nil && root . Right == nil {
if limit > 0 {
return nil
}
return root
}
root . Left = sufficientSubset ( root . Left , limit )
root . Right = sufficientSubset ( root . Right , limit )
if root . Left == nil && root . Right == nil {
return nil
}
return root
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function sufficientSubset ( root : TreeNode | null , limit : number ) : TreeNode | null {
if ( root === null ) {
return null ;
}
limit -= root . val ;
if ( root . left === null && root . right === null ) {
return limit > 0 ? null : root ;
}
root . left = sufficientSubset ( root . left , limit );
root . right = sufficientSubset ( root . right , limit );
return root . left === null && root . right === null ? null : root ;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25 /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {number} limit
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var sufficientSubset = function ( root , limit ) {
if ( root === null ) {
return null ;
}
limit -= root . val ;
if ( root . left === null && root . right === null ) {
return limit > 0 ? null : root ;
}
root . left = sufficientSubset ( root . left , limit );
root . right = sufficientSubset ( root . right , limit );
return root . left === null && root . right === null ? null : root ;
};