
题目描述
给定有向图的边 edges,以及该图的起点 source 和目标终点 destination,确定从起点 source 出发的所有路径是否最终结束于目标终点 destination,即:
- 从起点
source 到目标终点 destination 存在至少一条路径 - 如果存在从起点
source 到没有出边的节点的路径,则该节点就是路径终点。 - 从起点
source到目标终点 destination 可能路径数是有限数字
当从起点 source 出发的所有路径都可以到达目标终点 destination 时返回 true,否则返回 false。
示例 1:
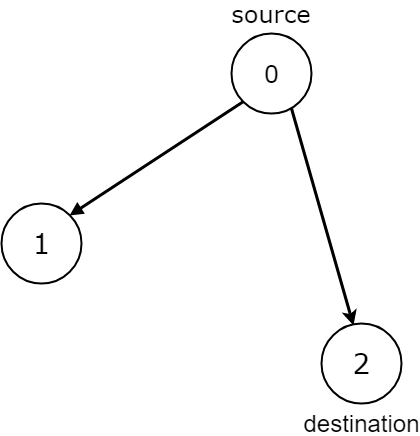
输入:n = 3, edges = [[0,1],[0,2]], source = 0, destination = 2
输出:false
说明:节点 1 和节点 2 都可以到达,但也会卡在那里。
示例 2:
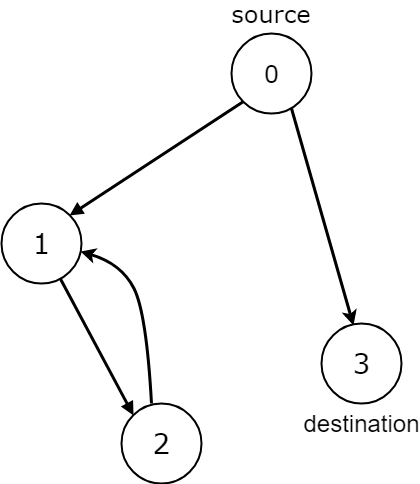
输入:n = 4, edges = [[0,1],[0,3],[1,2],[2,1]], source = 0, destination = 3
输出:false
说明:有两种可能:在节点 3 处结束,或是在节点 1 和节点 2 之间无限循环。
示例 3:
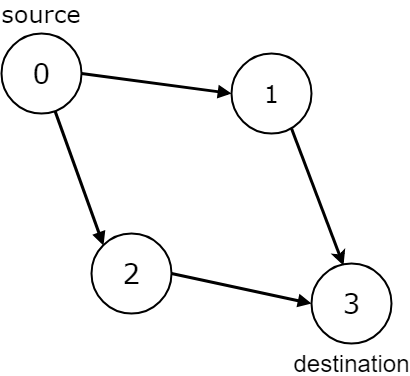
输入:n = 4, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,3],[2,3]], source = 0, destination = 3
输出:true
提示:
1 <= n <= 1040 <= edges.length <= 104edges[i].length == 20 <= ai, bi <= n - 10 <= source <= n - 10 <= destination <= n - 1- 给定的图中可能带有自环和平行边。
解法
方法一:DFS
我们用一个状态数组 \(\textit{state}\) 来记录每个节点的状态,其中:
- 状态 0 表示该节点未被访问过;
- 状态 1 表示该节点正在被访问;
- 状态 2 表示该节点已经被访问过且可以通向终点。
我们首先将图构建为邻接表的形式,然后从起点出发进行深度优先搜索(DFS)。在 DFS 过程中:
- 如果当前节点的状态为 1,说明我们遇到了一个环,直接返回 \(\text{false}\);
- 如果当前节点的状态为 2,说明该节点已经被访问过且可以通向终点,直接返回 \(\text{true}\);
- 如果当前节点没有出边,则检查该节点是否为终点,如果是则返回 \(\text{true}\),否则返回 \(\text{false}\);
- 否则,将当前节点的状态设为 1,递归访问所有相邻节点;
- 如果所有相邻节点都能通向终点,则将当前节点的状态设为 2 并返回 \(\text{true}\),否则返回 \(\text{false}\)。
答案为 \(\text{dfs}(\text{source})\) 的结果。
时间复杂度 \(O(n + m)\),其中 \(n\) 和 \(m\) 分别为节点数和边数。空间复杂度 \(O(n + m)\),用于存储图的邻接表和状态数组。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25 | class Solution:
def leadsToDestination(
self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]], source: int, destination: int
) -> bool:
def dfs(i: int) -> bool:
if st[i]:
return st[i] == 2
if not g[i]:
return i == destination
st[i] = 1
for j in g[i]:
if not dfs(j):
return False
st[i] = 2
return True
g = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for a, b in edges:
g[a].append(b)
if g[destination]:
return False
st = [0] * n
return dfs(source)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36 | class Solution {
private List<Integer>[] g;
private int[] st;
private int destination;
public boolean leadsToDestination(int n, int[][] edges, int source, int destination) {
this.destination = destination;
g = new List[n];
Arrays.setAll(g, k -> new ArrayList<>());
for (int[] e : edges) {
g[e[0]].add(e[1]);
}
if (!g[destination].isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
st = new int[n];
return dfs(source);
}
private boolean dfs(int i) {
if (st[i] != 0) {
return st[i] == 2;
}
if (g[i].isEmpty()) {
return i == destination;
}
st[i] = 1;
for (int j : g[i]) {
if (!dfs(j)) {
return false;
}
}
st[i] = 2;
return true;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36 | class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> g;
vector<int> st;
int destination;
bool leadsToDestination(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, int source, int destination) {
this->destination = destination;
g.assign(n, {});
for (auto& e : edges) {
g[e[0]].push_back(e[1]);
}
if (!g[destination].empty()) {
return false;
}
st.assign(n, 0);
return dfs(source);
}
bool dfs(int i) {
if (st[i] != 0) {
return st[i] == 2;
}
if (g[i].empty()) {
return i == destination;
}
st[i] = 1;
for (int j : g[i]) {
if (!dfs(j)) {
return false;
}
}
st[i] = 2;
return true;
}
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31 | func leadsToDestination(n int, edges [][]int, source int, destination int) bool {
g := make([][]int, n)
for _, e := range edges {
g[e[0]] = append(g[e[0]], e[1])
}
if len(g[destination]) > 0 {
return false
}
st := make([]int, n)
var dfs func(i int) bool
dfs = func(i int) bool {
if st[i] != 0 {
return st[i] == 2
}
if len(g[i]) == 0 {
return i == destination
}
st[i] = 1
for _, j := range g[i] {
if !dfs(j) {
return false
}
}
st[i] = 2
return true
}
return dfs(source)
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35 | function leadsToDestination(
n: number,
edges: number[][],
source: number,
destination: number,
): boolean {
const g: number[][] = Array.from({ length: n }, () => []);
for (const [a, b] of edges) {
g[a].push(b);
}
if (g[destination].length > 0) {
return false;
}
const st: number[] = Array(n).fill(0);
const dfs = (i: number): boolean => {
if (st[i] !== 0) {
return st[i] === 2;
}
if (g[i].length === 0) {
return i === destination;
}
st[i] = 1;
for (const j of g[i]) {
if (!dfs(j)) {
return false;
}
}
st[i] = 2;
return true;
};
return dfs(source);
}
|



