2509. Cycle Length Queries in a Tree
Description
You are given an integer n. There is a complete binary tree with 2n - 1 nodes. The root of that tree is the node with the value 1, and every node with a value val in the range [1, 2n - 1 - 1] has two children where:
- The left node has the value
2 * val, and - The right node has the value
2 * val + 1.
You are also given a 2D integer array queries of length m, where queries[i] = [ai, bi]. For each query, solve the following problem:
- Add an edge between the nodes with values
aiandbi. - Find the length of the cycle in the graph.
- Remove the added edge between nodes with values
aiandbi.
Note that:
- A cycle is a path that starts and ends at the same node, and each edge in the path is visited only once.
- The length of a cycle is the number of edges visited in the cycle.
- There could be multiple edges between two nodes in the tree after adding the edge of the query.
Return an array answer of length m where answer[i] is the answer to the ith query.
Example 1:
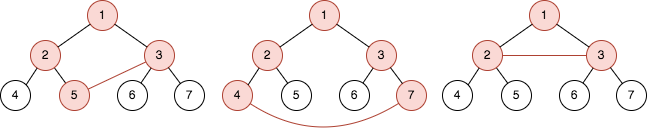
Input: n = 3, queries = [[5,3],[4,7],[2,3]] Output: [4,5,3] Explanation: The diagrams above show the tree of 23 - 1 nodes. Nodes colored in red describe the nodes in the cycle after adding the edge. - After adding the edge between nodes 3 and 5, the graph contains a cycle of nodes [5,2,1,3]. Thus answer to the first query is 4. We delete the added edge and process the next query. - After adding the edge between nodes 4 and 7, the graph contains a cycle of nodes [4,2,1,3,7]. Thus answer to the second query is 5. We delete the added edge and process the next query. - After adding the edge between nodes 2 and 3, the graph contains a cycle of nodes [2,1,3]. Thus answer to the third query is 3. We delete the added edge.
Example 2:
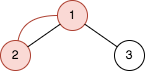
Input: n = 2, queries = [[1,2]] Output: [2] Explanation: The diagram above shows the tree of 22 - 1 nodes. Nodes colored in red describe the nodes in the cycle after adding the edge. - After adding the edge between nodes 1 and 2, the graph contains a cycle of nodes [2,1]. Thus answer for the first query is 2. We delete the added edge.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 30m == queries.length1 <= m <= 105queries[i].length == 21 <= ai, bi <= 2n - 1ai != bi
Solutions
Solution 1: Finding the Lowest Common Ancestor
For each query, we find the lowest common ancestor of the two nodes \(a\) and \(b\), and record the number of steps taken upwards. The answer to the query is the number of steps plus one.
To find the lowest common ancestor, if \(a > b\), we move \(a\) to its parent node; if \(a < b\), we move \(b\) to its parent node. We accumulate the number of steps until \(a = b\).
The time complexity is \(O(n \times m)\), where \(m\) is the length of the queries array.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | |