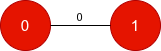3812. Minimum Edge Toggles on a Tree
Description
You are given an undirected tree with n nodes, numbered from 0 to n - 1. It is represented by a 2D integer array edges of length n - 1, where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the tree.
You are also given two binary strings start and target of length n. For each node x, start[x] is its initial color and target[x] is its desired color.
In one operation, you may pick an edge with index i and toggle both of its endpoints. That is, if the edge is [u, v], then the colors of nodes u and v each flip from '0' to '1' or from '1' to '0'.
Return an array of edge indices whose operations transform start into target. Among all valid sequences with minimum possible length, return the edge indices in increasing order.
If it is impossible to transform start into target, return an array containing a single element equal to -1.
Example 1:
Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1],[1,2]], start = "010", target = "100"
Output: [0]
Explanation:
Toggle edge with index 0, which flips nodes 0 and 1.
The string changes from "010" to "100", matching the target.
Example 2:
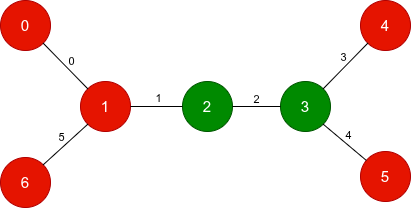
Input: n = 7, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[3,5],[1,6]], start = "0011000", target = "0010001"
Output: [1,2,5]
Explanation:
- Toggle edge with index 1, which flips nodes 1 and 2.
- Toggle edge with index 2, which flips nodes 2 and 3.
- Toggle edge with index 5, which flips nodes 1 and 6.
After these operations, the resulting string becomes "0010001", which matches the target.
Example 3:
Input: n = 2, edges = [[0,1]], start = "00", target = "01"
Output: [-1]
Explanation:
There is no sequence of edge toggles that transforms "00" into "01". Therefore, we return [-1].
Constraints:
2 <= n == start.length == target.length <= 105edges.length == n - 1edges[i] = [ai, bi]0 <= ai, bi < nstart[i]is either'0'or'1'.target[i]is either'0'or'1'.- The input is generated such that
edgesrepresents a valid tree.
Solutions
Solution 1: DFS
We define an adjacency list \(g\) to represent the tree, where \(g[a]\) stores all adjacent nodes of node \(a\) and the indices of the corresponding edges.
We design a function \(\text{dfs}(a, \text{fa})\), which indicates whether the edge between node \(a\) and \(\text{fa}\) needs to be toggled in the subtree rooted at node \(a\) with parent \(\text{fa}\). The logic of the function \(\text{dfs}(a, \text{fa})\) is as follows:
- Initialize a boolean variable \(\text{rev}\), indicating whether node \(a\) needs to be toggled. The initial value is \(\text{start}[a] \ne \text{target}[a]\).
- Iterate through all adjacent nodes \(b\) of node \(a\) and the corresponding edge index \(i\):
- If \(b \ne \text{fa}\), recursively call \(\text{dfs}(b, a)\).
- If the recursive call returns true, it means the edge \([a, b]\) in the subtree needs to be toggled. We add the edge index \(i\) to the answer list and toggle \(\text{rev}\).
- Return \(\text{rev}\).
Finally, we call \(\text{dfs}(0, -1)\). If the return value is true, it means it is impossible to convert \(\text{start}\) to \(\text{target}\), so we return \([-1]\). Otherwise, we sort the answer list and return it.
The time complexity is \(O(n \times \log n)\), and the space complexity is \(O(n)\). Here, \(n\) is the number of nodes in the tree.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | |