


题目描述
由于一个漏洞,文件系统中存在许多重复文件夹。给你一个二维数组 paths,其中 paths[i] 是一个表示文件系统中第 i 个文件夹的绝对路径的数组。
- 例如,
["one", "two", "three"] 表示路径 "/one/two/three" 。
如果两个文件夹(不需要在同一层级)包含 非空且相同的 子文件夹 集合 并具有相同的子文件夹结构,则认为这两个文件夹是相同文件夹。相同文件夹的根层级 不 需要相同。如果存在两个(或两个以上)相同 文件夹,则需要将这些文件夹和所有它们的子文件夹 标记 为待删除。
- 例如,下面文件结构中的文件夹
"/a" 和 "/b" 相同。它们(以及它们的子文件夹)应该被 全部 标记为待删除: /a/a/x/a/x/y/a/z/b/b/x/b/x/y/b/z
- 然而,如果文件结构中还包含路径
"/b/w" ,那么文件夹 "/a" 和 "/b" 就不相同。注意,即便添加了新的文件夹 "/b/w" ,仍然认为 "/a/x" 和 "/b/x" 相同。
一旦所有的相同文件夹和它们的子文件夹都被标记为待删除,文件系统将会 删除 所有上述文件夹。文件系统只会执行一次删除操作。执行完这一次删除操作后,不会删除新出现的相同文件夹。
返回二维数组 ans ,该数组包含删除所有标记文件夹之后剩余文件夹的路径。路径可以按 任意顺序 返回。
示例 1:
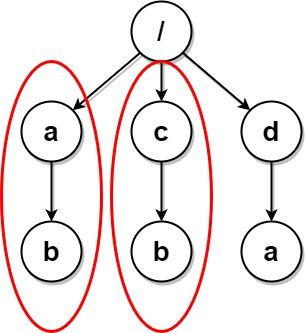
输入:paths = [["a"],["c"],["d"],["a","b"],["c","b"],["d","a"]]
输出:[["d"],["d","a"]]
解释:文件结构如上所示。
文件夹 "/a" 和 "/c"(以及它们的子文件夹)都会被标记为待删除,因为它们都包含名为 "b" 的空文件夹。
示例 2:
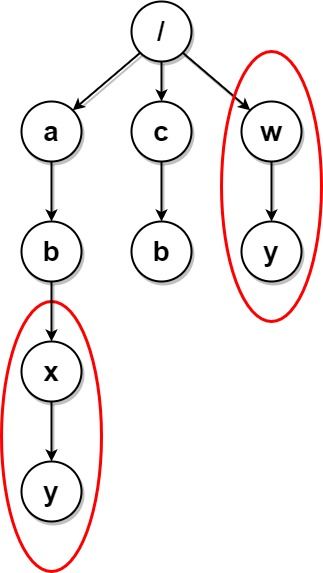
输入:paths = [["a"],["c"],["a","b"],["c","b"],["a","b","x"],["a","b","x","y"],["w"],["w","y"]]
输出:[["c"],["c","b"],["a"],["a","b"]]
解释:文件结构如上所示。
文件夹 "/a/b/x" 和 "/w"(以及它们的子文件夹)都会被标记为待删除,因为它们都包含名为 "y" 的空文件夹。
注意,文件夹 "/a" 和 "/c" 在删除后变为相同文件夹,但这两个文件夹不会被删除,因为删除只会进行一次,且它们没有在删除前被标记。
示例 3:
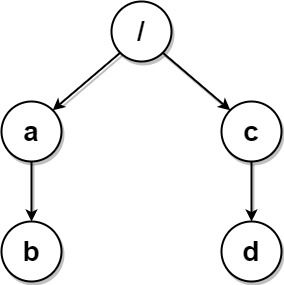
输入:paths = [["a","b"],["c","d"],["c"],["a"]]
输出:[["c"],["c","d"],["a"],["a","b"]]
解释:文件系统中所有文件夹互不相同。
注意,返回的数组可以按不同顺序返回文件夹路径,因为题目对顺序没有要求。
示例 4:
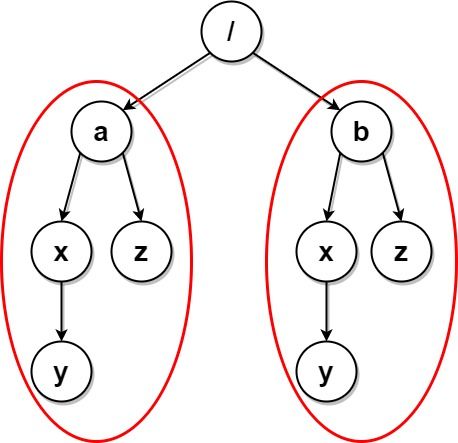
输入:paths = [["a"],["a","x"],["a","x","y"],["a","z"],["b"],["b","x"],["b","x","y"],["b","z"]]
输出:[]
解释:文件结构如上所示。
文件夹 "/a/x" 和 "/b/x"(以及它们的子文件夹)都会被标记为待删除,因为它们都包含名为 "y" 的空文件夹。
文件夹 "/a" 和 "/b"(以及它们的子文件夹)都会被标记为待删除,因为它们都包含一个名为 "z" 的空文件夹以及上面提到的文件夹 "x" 。
示例 5:
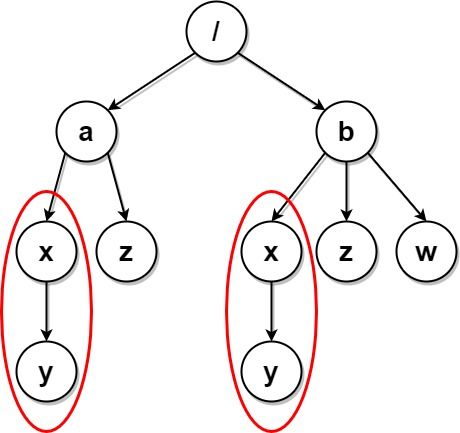
输入:paths = [["a"],["a","x"],["a","x","y"],["a","z"],["b"],["b","x"],["b","x","y"],["b","z"],["b","w"]]
输出:[["b"],["b","w"],["b","z"],["a"],["a","z"]]
解释:本例与上例的结构基本相同,除了新增 "/b/w" 文件夹。
文件夹 "/a/x" 和 "/b/x" 仍然会被标记,但 "/a" 和 "/b" 不再被标记,因为 "/b" 中有名为 "w" 的空文件夹而 "/a" 没有。
注意,"/a/z" 和 "/b/z" 不会被标记,因为相同子文件夹的集合必须是非空集合,但这两个文件夹都是空的。
提示:
1 <= paths.length <= 2 * 1041 <= paths[i].length <= 5001 <= paths[i][j].length <= 101 <= sum(paths[i][j].length) <= 2 * 105path[i][j] 由小写英文字母组成- 不会存在两个路径都指向同一个文件夹的情况
- 对于不在根层级的任意文件夹,其父文件夹也会包含在输入中
解法
方法一:字典树 + DFS
我们可以使用字典树来存储文件夹的结构,字典树的每个节点数据如下:
children:一个字典,键为子文件夹的名称,值为对应的子节点。deleted:一个布尔值,表示该节点是否被标记为待删除。
我们将所有路径插入到字典树中,然后使用 DFS 遍历字典树,构建每个子树的字符串表示。对于每个子树,如果它的字符串表示已经存在于一个全局字典中,则将该节点和全局字典中的对应节点都标记为待删除。最后,再次使用 DFS 遍历字典树,将未被标记的节点的路径添加到结果列表中。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46 | class Trie:
def __init__(self):
self.children: Dict[str, "Trie"] = defaultdict(Trie)
self.deleted: bool = False
class Solution:
def deleteDuplicateFolder(self, paths: List[List[str]]) -> List[List[str]]:
root = Trie()
for path in paths:
cur = root
for name in path:
if cur.children[name] is None:
cur.children[name] = Trie()
cur = cur.children[name]
g: Dict[str, Trie] = {}
def dfs(node: Trie) -> str:
if not node.children:
return ""
subs: List[str] = []
for name, child in node.children.items():
subs.append(f"{name}({dfs(child)})")
s = "".join(sorted(subs))
if s in g:
node.deleted = g[s].deleted = True
else:
g[s] = node
return s
def dfs2(node: Trie) -> None:
if node.deleted:
return
if path:
ans.append(path[:])
for name, child in node.children.items():
path.append(name)
dfs2(child)
path.pop()
dfs(root)
ans: List[List[str]] = []
path: List[str] = []
dfs2(root)
return ans
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75 | class Trie {
Map<String, Trie> children;
boolean deleted;
public Trie() {
children = new HashMap<>();
deleted = false;
}
}
class Solution {
public List<List<String>> deleteDuplicateFolder(List<List<String>> paths) {
Trie root = new Trie();
for (List<String> path : paths) {
Trie cur = root;
for (String name : path) {
if (!cur.children.containsKey(name)) {
cur.children.put(name, new Trie());
}
cur = cur.children.get(name);
}
}
Map<String, Trie> g = new HashMap<>();
var dfs = new Function<Trie, String>() {
@Override
public String apply(Trie node) {
if (node.children.isEmpty()) {
return "";
}
List<String> subs = new ArrayList<>();
for (var entry : node.children.entrySet()) {
subs.add(entry.getKey() + "(" + apply(entry.getValue()) + ")");
}
Collections.sort(subs);
String s = String.join("", subs);
if (g.containsKey(s)) {
node.deleted = true;
g.get(s).deleted = true;
} else {
g.put(s, node);
}
return s;
}
};
dfs.apply(root);
List<List<String>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> path = new ArrayList<>();
var dfs2 = new Function<Trie, Void>() {
@Override
public Void apply(Trie node) {
if (node.deleted) {
return null;
}
if (!path.isEmpty()) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
}
for (Map.Entry<String, Trie> entry : node.children.entrySet()) {
path.add(entry.getKey());
apply(entry.getValue());
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
return null;
}
};
dfs2.apply(root);
return ans;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65 | class Trie {
public:
unordered_map<string, Trie*> children;
bool deleted = false;
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<string>> deleteDuplicateFolder(vector<vector<string>>& paths) {
Trie* root = new Trie();
for (auto& path : paths) {
Trie* cur = root;
for (auto& name : path) {
if (cur->children.find(name) == cur->children.end()) {
cur->children[name] = new Trie();
}
cur = cur->children[name];
}
}
unordered_map<string, Trie*> g;
auto dfs = [&](this auto&& dfs, Trie* node) -> string {
if (node->children.empty()) return "";
vector<string> subs;
for (auto& child : node->children) {
subs.push_back(child.first + "(" + dfs(child.second) + ")");
}
sort(subs.begin(), subs.end());
string s = "";
for (auto& sub : subs) s += sub;
if (g.contains(s)) {
node->deleted = true;
g[s]->deleted = true;
} else {
g[s] = node;
}
return s;
};
dfs(root);
vector<vector<string>> ans;
vector<string> path;
auto dfs2 = [&](this auto&& dfs2, Trie* node) -> void {
if (node->deleted) return;
if (!path.empty()) {
ans.push_back(path);
}
for (auto& child : node->children) {
path.push_back(child.first);
dfs2(child.second);
path.pop_back();
}
};
dfs2(root);
return ans;
}
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62 | type Trie struct {
children map[string]*Trie
deleted bool
}
func NewTrie() *Trie {
return &Trie{
children: make(map[string]*Trie),
}
}
func deleteDuplicateFolder(paths [][]string) (ans [][]string) {
root := NewTrie()
for _, path := range paths {
cur := root
for _, name := range path {
if _, exists := cur.children[name]; !exists {
cur.children[name] = NewTrie()
}
cur = cur.children[name]
}
}
g := make(map[string]*Trie)
var dfs func(*Trie) string
dfs = func(node *Trie) string {
if len(node.children) == 0 {
return ""
}
var subs []string
for name, child := range node.children {
subs = append(subs, name+"("+dfs(child)+")")
}
sort.Strings(subs)
s := strings.Join(subs, "")
if existingNode, exists := g[s]; exists {
node.deleted = true
existingNode.deleted = true
} else {
g[s] = node
}
return s
}
var dfs2 func(*Trie, []string)
dfs2 = func(node *Trie, path []string) {
if node.deleted {
return
}
if len(path) > 0 {
ans = append(ans, append([]string{}, path...))
}
for name, child := range node.children {
dfs2(child, append(path, name))
}
}
dfs(root)
dfs2(root, []string{})
return ans
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60 | function deleteDuplicateFolder(paths: string[][]): string[][] {
class Trie {
children: { [key: string]: Trie } = {};
deleted: boolean = false;
}
const root = new Trie();
for (const path of paths) {
let cur = root;
for (const name of path) {
if (!cur.children[name]) {
cur.children[name] = new Trie();
}
cur = cur.children[name];
}
}
const g: { [key: string]: Trie } = {};
const dfs = (node: Trie): string => {
if (Object.keys(node.children).length === 0) return '';
const subs: string[] = [];
for (const [name, child] of Object.entries(node.children)) {
subs.push(`${name}(${dfs(child)})`);
}
subs.sort();
const s = subs.join('');
if (g[s]) {
node.deleted = true;
g[s].deleted = true;
} else {
g[s] = node;
}
return s;
};
dfs(root);
const ans: string[][] = [];
const path: string[] = [];
const dfs2 = (node: Trie): void => {
if (node.deleted) return;
if (path.length > 0) {
ans.push([...path]);
}
for (const [name, child] of Object.entries(node.children)) {
path.push(name);
dfs2(child);
path.pop();
}
};
dfs2(root);
return ans;
}
|







