999. Available Captures for Rook
Description
You are given an 8 x 8 matrix representing a chessboard. There is exactly one white rook represented by 'R', some number of white bishops 'B', and some number of black pawns 'p'. Empty squares are represented by '.'.
A rook can move any number of squares horizontally or vertically (up, down, left, right) until it reaches another piece or the edge of the board. A rook is attacking a pawn if it can move to the pawn's square in one move.
Note: A rook cannot move through other pieces, such as bishops or pawns. This means a rook cannot attack a pawn if there is another piece blocking the path.
Return the number of pawns the white rook is attacking.
Example 1:
Input: board = [[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".","p",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".","R",".",".",".","p"],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".","p",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."]]
Output: 3
Explanation:
In this example, the rook is attacking all the pawns.
Example 2:
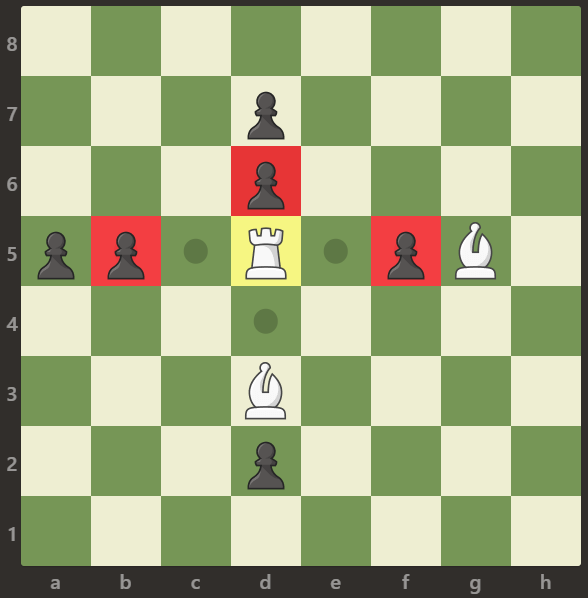
Input: board = [[".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".","p","p","p","p","p",".","."],[".","p","p","B","p","p",".","."],[".","p","B","R","B","p",".","."],[".","p","p","B","p","p",".","."],[".","p","p","p","p","p",".","."],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."]]
Output: 0
Explanation:
The bishops are blocking the rook from attacking any of the pawns.
Example 3:
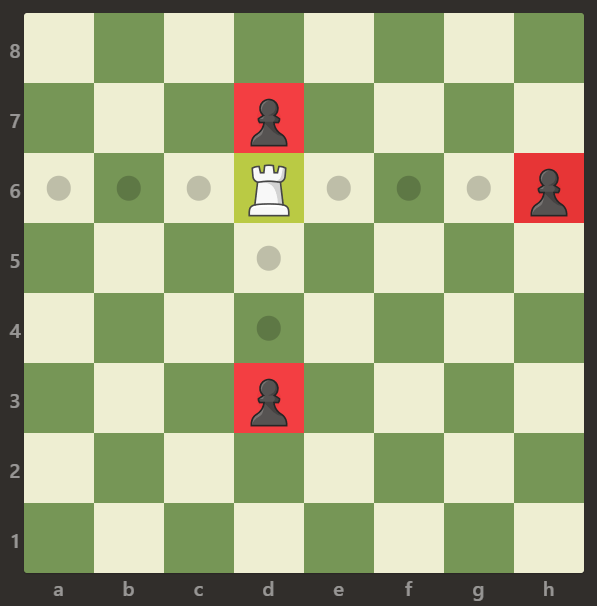
Input: board = [[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".","p",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".","p",".",".",".","."],["p","p",".","R",".","p","B","."],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".","B",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".","p",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."]]
Output: 3
Explanation:
The rook is attacking the pawns at positions b5, d6, and f5.
Constraints:
board.length == 8board[i].length == 8board[i][j]is either'R','.','B', or'p'- There is exactly one cell with
board[i][j] == 'R'
Solutions
Solution 1: Simulation
We first traverse the board to find the position of the rook \((i, j)\). Then, starting from \((i, j)\), we traverse in four directions: up, down, left, and right.
- If it is not the boundary and not a bishop, continue moving forward.
- If it is a pawn, increment the answer by one and stop traversing in that direction.
After traversing in all four directions, we get the answer.
The time complexity is \(O(m \times n)\), where \(m\) and \(n\) are the number of rows and columns of the board, respectively. In this problem, \(m = n = 8\). The space complexity is \(O(1)\).
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 | |