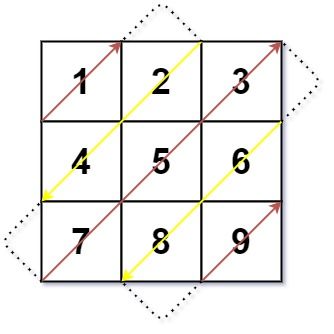
Array Matrix Simulation
Description Given an m x n matrix mat, return an array of all the elements of the array in a diagonal order .
Example 1:
Input: mat = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
Output: [1,2,4,7,5,3,6,8,9]
Example 2:
Input: mat = [[1,2],[3,4]]
Output: [1,2,3,4]
Constraints:
m == mat.lengthn == mat[i].length1 <= m, n <= 104 1 <= m * n <= 104 -105 <= mat[i][j] <= 105 Solutions Solution 1: Fixed Point Traversal For each round \(k\) , we fix the starting point from the top-right and traverse diagonally to the bottom-left to get \(t\) . If \(k\) is even, we reverse \(t\) .
The time complexity is \(O(m \times n)\) , and the space complexity is \(O(1)\) . Ignoring the space used for the answer.
Python3 Java C++ Go TypeScript Rust C#
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16 class Solution :
def findDiagonalOrder ( self , mat : List [ List [ int ]]) -> List [ int ]:
m , n = len ( mat ), len ( mat [ 0 ])
ans = []
for k in range ( m + n - 1 ):
t = []
i = 0 if k < n else k - n + 1
j = k if k < n else n - 1
while i < m and j >= 0 :
t . append ( mat [ i ][ j ])
i += 1
j -= 1
if k % 2 == 0 :
t = t [:: - 1 ]
ans . extend ( t )
return ans
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25 class Solution {
public int [] findDiagonalOrder ( int [][] mat ) {
int m = mat . length , n = mat [ 0 ] . length ;
int [] ans = new int [ m * n ] ;
int idx = 0 ;
List < Integer > t = new ArrayList <> ();
for ( int k = 0 ; k < m + n - 1 ; ++ k ) {
int i = k < n ? 0 : k - n + 1 ;
int j = k < n ? k : n - 1 ;
while ( i < m && j >= 0 ) {
t . add ( mat [ i ][ j ] );
++ i ;
-- j ;
}
if ( k % 2 == 0 ) {
Collections . reverse ( t );
}
for ( int v : t ) {
ans [ idx ++] = v ;
}
t . clear ();
}
return ans ;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24 class Solution {
public :
vector < int > findDiagonalOrder ( vector < vector < int >>& mat ) {
int m = mat . size ();
int n = mat [ 0 ]. size ();
vector < int > ans ;
vector < int > t ;
for ( int k = 0 ; k < m + n - 1 ; ++ k ) {
int i = ( k < n ) ? 0 : k - n + 1 ;
int j = ( k < n ) ? k : n - 1 ;
while ( i < m && j >= 0 ) {
t . push_back ( mat [ i ][ j ]);
++ i ;
-- j ;
}
if ( k % 2 == 0 ) {
ranges :: reverse ( t );
}
ans . insert ( ans . end (), t . begin (), t . end ());
t . clear ();
}
return ans ;
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26 func findDiagonalOrder ( mat [][] int ) [] int {
m := len ( mat )
n := len ( mat [ 0 ])
ans := make ([] int , 0 , m * n )
for k := 0 ; k < m + n - 1 ; k ++ {
t := make ([] int , 0 )
var i , j int
if k < n {
i = 0
j = k
} else {
i = k - n + 1
j = n - 1
}
for i < m && j >= 0 {
t = append ( t , mat [ i ][ j ])
i ++
j --
}
if k % 2 == 0 {
slices . Reverse ( t )
}
ans = append ( ans , t ... )
}
return ans
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20 function findDiagonalOrder ( mat : number [][]) : number [] {
const m = mat . length ;
const n = mat [ 0 ]. length ;
const ans : number [] = [];
for ( let k = 0 ; k < m + n - 1 ; k ++ ) {
const t : number [] = [];
let i = k < n ? 0 : k - n + 1 ;
let j = k < n ? k : n - 1 ;
while ( i < m && j >= 0 ) {
t . push ( mat [ i ][ j ]);
i ++ ;
j -- ;
}
if ( k % 2 === 0 ) {
t . reverse ();
}
ans . push (... t );
}
return ans ;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26 impl Solution {
pub fn find_diagonal_order ( mat : Vec < Vec < i32 >> ) -> Vec < i32 > {
let m = mat . len ();
let n = mat [ 0 ]. len ();
let mut ans = Vec :: with_capacity ( m * n );
for k in 0 .. ( m + n - 1 ) {
let mut t = Vec :: new ();
let ( mut i , mut j ) = if k < n {
( 0 , k )
} else {
( k - n + 1 , n - 1 )
};
while i < m && j < n {
t . push ( mat [ i ][ j ]);
i += 1 ;
if j == 0 { break ; }
j -= 1 ;
}
if k % 2 == 0 {
t . reverse ();
}
ans . extend ( t );
}
ans
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22 public class Solution {
public int [] FindDiagonalOrder ( int [][] mat ) {
int m = mat . Length ;
int n = mat [ 0 ]. Length ;
List < int > ans = new List < int > ();
for ( int k = 0 ; k < m + n - 1 ; k ++ ) {
List < int > t = new List < int > ();
int i = k < n ? 0 : k - n + 1 ;
int j = k < n ? k : n - 1 ;
while ( i < m && j >= 0 ) {
t . Add ( mat [ i ][ j ]);
i ++ ;
j -- ;
}
if ( k % 2 == 0 ) {
t . Reverse ();
}
ans . AddRange ( t );
}
return ans . ToArray ();
}
}
GitHub