3650. Minimum Cost Path with Edge Reversals
Description
You are given a directed, weighted graph with n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1, and an array edges where edges[i] = [ui, vi, wi] represents a directed edge from node ui to node vi with cost wi.
Each node ui has a switch that can be used at most once: when you arrive at ui and have not yet used its switch, you may activate it on one of its incoming edges vi → ui reverse that edge to ui → vi and immediately traverse it.
The reversal is only valid for that single move, and using a reversed edge costs 2 * wi.
Return the minimum total cost to travel from node 0 to node n - 1. If it is not possible, return -1.
Example 1:
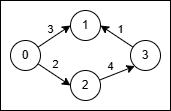
Input: n = 4, edges = [[0,1,3],[3,1,1],[2,3,4],[0,2,2]]
Output: 5
Explanation:
- Use the path
0 → 1(cost 3). - At node 1 reverse the original edge
3 → 1into1 → 3and traverse it at cost2 * 1 = 2. - Total cost is
3 + 2 = 5.
Example 2:
Input: n = 4, edges = [[0,2,1],[2,1,1],[1,3,1],[2,3,3]]
Output: 3
Explanation:
- No reversal is needed. Take the path
0 → 2(cost 1), then2 → 1(cost 1), then1 → 3(cost 1). - Total cost is
1 + 1 + 1 = 3.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 5 * 1041 <= edges.length <= 105edges[i] = [ui, vi, wi]0 <= ui, vi <= n - 11 <= wi <= 1000
Solutions
Solution 1: Dijkstra's Algorithm
According to the problem description, we can construct a directed graph \(g\) where each edge \((u, v)\) allows for two types of traversal:
- Direct traversal with cost \(w\), corresponding to edge \((u, v)\).
- Reverse traversal with cost \(2w\), corresponding to edge \((v, u)\).
Then, we can use Dijkstra's algorithm on graph \(g\) to find the shortest path from node \(0\) to node \(n-1\), which corresponds to the minimum total cost required.
Specifically, we define a priority queue \(pq\), where each element is a tuple \((d, u)\), indicating that the current minimum cost to reach node \(u\) is \(d\). We also define an array \(\textit{dist}\), where \(\textit{dist}[u]\) represents the minimum cost from node \(0\) to node \(u\). Initially, we set \(\textit{dist}[0] = 0\), and the costs for all other nodes to infinity, then push \((0, 0)\) into the queue.
In each iteration, we extract the node \((d, u)\) with the minimum cost from the priority queue. If \(d\) is greater than \(\textit{dist}[u]\), we skip this node. Otherwise, we traverse all neighbors \(v\) of node \(u\), calculating the new cost \(nd = d + w\) to reach node \(v\) via node \(u\). If \(nd\) is less than \(\textit{dist}[v]\), we update \(\textit{dist}[v] = nd\) and push \((nd, v)\) into the queue.
When we extract node \(n-1\), the current \(d\) is the minimum total cost from node \(0\) to node \(n-1\). If the priority queue becomes empty and node \(n-1\) has not been extracted, it implies that node \(n-1\) is unreachable, so we return -1.
The time complexity is \(O(n + m \times \log m)\), and the space complexity is \(O(n + m)\). Here, \(n\) and \(m\) refer to the number of nodes and edges, respectively.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 | |