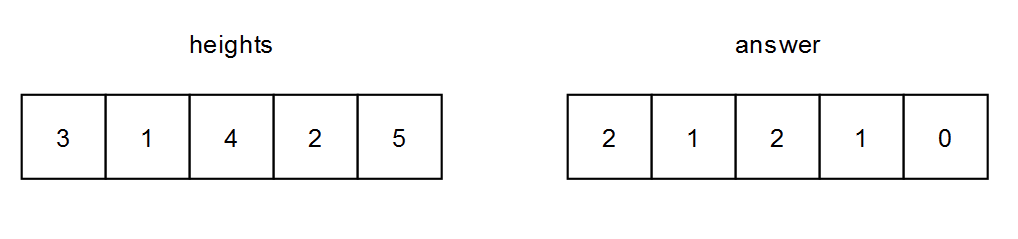2282. Number of People That Can Be Seen in a Grid 🔒
Description
You are given an m x n 0-indexed 2D array of positive integers heights where heights[i][j] is the height of the person standing at position (i, j).
A person standing at position (row1, col1) can see a person standing at position (row2, col2) if:
- The person at
(row2, col2)is to the right or below the person at(row1, col1). More formally, this means that eitherrow1 == row2andcol1 < col2orrow1 < row2andcol1 == col2. - Everyone in between them is shorter than both of them.
Return an m x n 2D array of integers answer where answer[i][j] is the number of people that the person at position (i, j) can see.
Example 1:
Input: heights = [[3,1,4,2,5]] Output: [[2,1,2,1,0]] Explanation: - The person at (0, 0) can see the people at (0, 1) and (0, 2). Note that he cannot see the person at (0, 4) because the person at (0, 2) is taller than him. - The person at (0, 1) can see the person at (0, 2). - The person at (0, 2) can see the people at (0, 3) and (0, 4). - The person at (0, 3) can see the person at (0, 4). - The person at (0, 4) cannot see anybody.
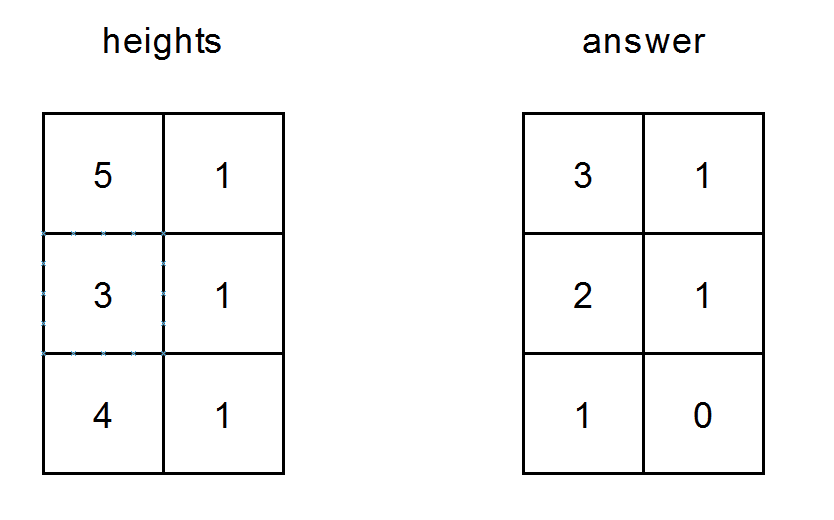
Example 2:
Input: heights = [[5,1],[3,1],[4,1]] Output: [[3,1],[2,1],[1,0]] Explanation: - The person at (0, 0) can see the people at (0, 1), (1, 0) and (2, 0). - The person at (0, 1) can see the person at (1, 1). - The person at (1, 0) can see the people at (1, 1) and (2, 0). - The person at (1, 1) can see the person at (2, 1). - The person at (2, 0) can see the person at (2, 1). - The person at (2, 1) cannot see anybody.
Constraints:
1 <= heights.length <= 4001 <= heights[i].length <= 4001 <= heights[i][j] <= 105
Solutions
Solution 1: Monotonic Stack
We observe that for the \(i\)-th person, the people he can see must have heights that are strictly monotonically increasing from left to right (or from top to bottom).
Therefore, for each row, we can use a monotonic stack to find the number of people each person can see.
Specifically, we can traverse the array in reverse order, using a stack \(stk\) that is monotonically increasing from top to bottom to record the heights of the people we have traversed.
For the \(i\)-th person, if the stack is not empty and the top element of the stack is less than \(heights[i]\), we increment the number of people the \(i\)-th person can see, and then pop the top element of the stack, repeating this until the stack is empty or the top element of the stack is greater than or equal to \(heights[i]\). If the stack is not empty at this point, it means the top element of the stack is greater than or equal to \(heights[i]\), so we increment the number of people the \(i\)-th person can see by 1. Next, if the stack is not empty and the top element of the stack is equal to \(heights[i]\), we pop the top element of the stack. Finally, we push \(heights[i]\) onto the stack and continue to the next person.
After processing this way, we can get the number of people each person can see for each row.
Similarly, we can process each column to get the number of people each person can see for each column. Finally, we add the answers for each row and each column to get the final answer.
The time complexity is \(O(m \times n)\), and the space complexity is \(O(\max(m, n))\). Where \(m\) and \(n\) are the number of rows and columns of the array \(heights\), respectively.
Similar problems:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 | |